Why Buildings collapse and how to avoid it

About Course
‘Because of Buildings not being tied properly’
Course Description
The structure of buildings; How buildings stand up; Anchoring of buildings into the ground in various materials; Importance of foundation; rigidity in the structure; how loads are transferred within the structure; where weaknesses occur; the importance of material quality; How materials acquire weakness; mixing of concrete and its importance; curing and its importance; checking the quality of material; good workmanship; importance of involving professionals.
Goals
- The purpose of this course is to deliver sufficient knowledge to builders to prevent buildings from collapsing while under construction by highlighting and explaining the main causes of collapse.
- The course also aims to sensitize builders on the role of professional consultants and the critical moments when their input must be sought.
Target learners
The target audience for the course are people involved in site work. This course is especially targeted at site managers, site supervisors, foremen, clerks of works. However the course is appropriate for all people who are involved in any way with the process of building but have not undergone a formal training programme. The course is delivered in simple language suitable for those who need to understand basic principles of the building process.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, learners will be able to:
- Explain how buildings are able to stand up
- Understand the critical points for alertness in the building process to avert later dangers.
- Understand the critical moments that must be referred to professionals to minimize the risks of bad decisions.
Course Structure
SESSION 1. INTRODUCTION

- How are buildings anchored?
- Structure composition
- Loads types and transfer
- Site selection and Foundations
- Joinery (welding, nailing)
SESSION 2. THE STRUCTURE OF A BUILDING

- How buildings stand up
- Anchoring of buildings into the ground in various materials;
- Rigidity in the structure;
- Where weaknesses occur;
SESSION 3. FOUNDATIONS
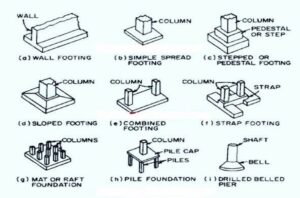
- Importance of foundation;
- Types of foundation
- Type of soil
- Differential settlements
SESSION 4. LOADS
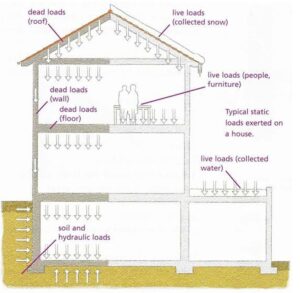
SESSION 5. MATERIAL SPECIFICATIONS/QUALITY

- How materials acquire weakness;
- checking the quality of material;
- Deterioration of materials e.g., timber (weather elements), concrete(old), steel(rust)
SESSION 6. CONCRETE/STEEL
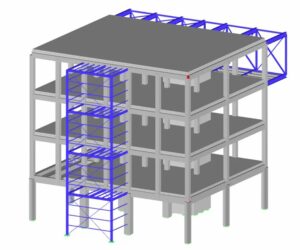
- mixing of concrete and its importance;
- curing and its importance;
- Sub-standard Concrete mixing ratios
SESSION 7. PROFESSIONALS

- Good workmanship;
- Importance of involving professionals.
SESSION 8. THREATS/MAN-MADE HAZARDS

- Bad material uses
- Groundwater/site selection vs solid rock base
- Poor workmanship
SESSION 9. NATURAL HAZARDS

- Fire-Proofing buildings
- Earthquake Resistant buildings
- Flooding Resistant buildings
- Tornadoes
- Hurricanes
SESSION 10. CONCLUSION
1. Evaluation
Course Content
SESSION 1: INTRODUCTION
-
1.Structure composition
-
2. Loads types and transfer
-
3. Site selection and Foundations
-
4. Joinery (welding, nailing)
-
5. Chapter 1 Questions
